Data integrity vs. data quality: Is there a difference?
IBM Journey to AI blog
JULY 13, 2023
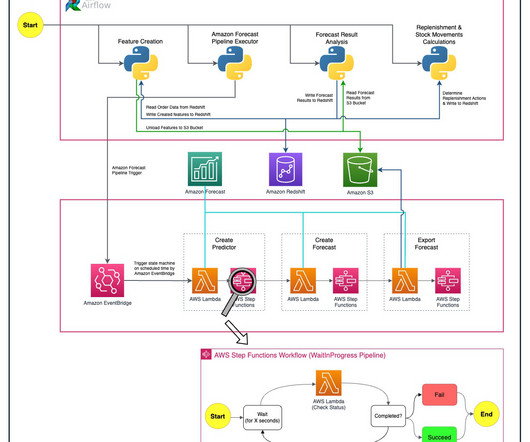
When we talk about data integrity, we’re referring to the overarching completeness, accuracy, consistency, accessibility, and security of an organization’s data. Together, these factors determine the reliability of the organization’s data. In short, yes.























Let's personalize your content